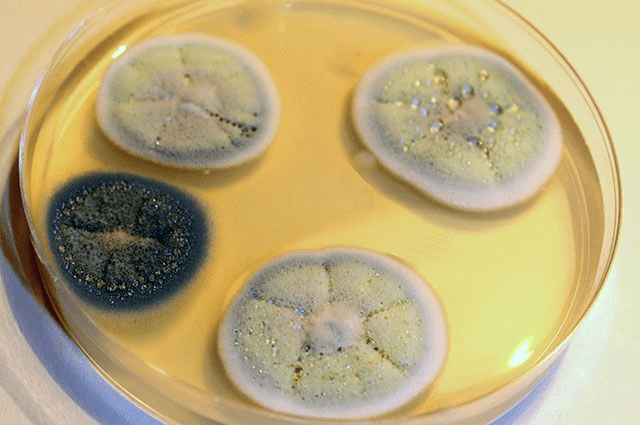
If you look closely at the entire history of medicine, you will not be able to find a single remedy as effective as penicillin, which would save so many human lives. Oddly enough, penicillin was named after the mold, the spores of which can be found in the air, Penicillium. The discovery of penicillin is also the merit of Fleming, in whose laboratory the history of the appearance of this substance began.
History of the discovery of penicillin
Penicillin is an antibiotic that has the widest range of action, it is able to cure such serious diseases as syphilis, gangrene, infections with staphylococci and streptococci. Many do not know that the antibiotic got its name for a reason, it was named after the mold fungus from which it is obtained.
In history, penicillin has played a huge role, as at all times it helped to save human lives. Even in the written documents of the ancient Persian medical scientist Avicenna (Abu-Ali-ibn-Sina), as well as the Swiss scientist Paracelsus, there are references to the healing properties of mold, although at that time the fungus had not yet been processed into a drug and did not get its own name.
Fleming’s penicillin was repeatedly invented by other scientists long before him. In 1896, Bartolomeo Gazio carried out studies of mold damage to rice. Based on his research, he deduced an antibiotic formula that was almost identical to modern penicillin. However, his invention did not find recognition, since it was not decided where and how to apply it.
In 1897, the French physician Ernest Duchene noticed the entertaining activity of Arab grooms – they collected mold from saddles, and then healed the wounds of animals with it. Obviously, the Arabs learned about the healing properties of mold from Avicenna, carrying his invaluable knowledge through the centuries. Duchenne did not stop at his remark. He decided to investigate how mold could affect puking. As a result, according to the results of his experiments, he realized that mold is a serious enemy for typhoid fever bacillus. Duchenne discovered penicillin, but his discovery also did not find recognition.
In 1913, Carl Alsberg and Otis Fischer Black, scientists from the United States of America, almost succeeded in inventing a mold-based medicine, but their research was interrupted as the First World War began.
Watch the video about the discovery of penicillin.
In 1928, British scientist Alexander Fleming discovered the killer properties of mold for staphylococci literally by his own negligence. He conducted experiments on how the human body can resist infectious diseases. One day, he discovered that the calyx staphylococci he had left in the lab were being attacked by the mold Penicillium. Upon closer examination, it became clear that there were no sticks around the mold formation of the brush. The destructive substance that fungi produced, he called penicillin.
Underestimating the significance of his discovery, Fleming decided that it would be incredibly difficult to obtain an antibiotic from this substance. Thus, further research was carried out by Oxford scientists, who were able to extract the substance in its pure form and investigate its properties.
The first penicillin vaccine was given on February 12, 1941 to a policeman who was dying of blood poisoning. He really felt better from the substance, but due to the small amount of the drug, it was not possible to save him.
In 1945, Alexander Fleming, Howard Florey and Ernst Chain received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for discovering penicillin, the strongest antibiotic in history.
Fleming’s penicillin: action and use
Penicillin, a group of penicillins, has an action that kills pathogenic microorganisms. It affects the proteins of bacteria, blocking the synthesis and construction of cell walls, due to which the microorganism dies.
Indications for use: the antibiotic penicillin, its use is very common in practical medicine today. This is the most effective bactericidal agent. It is indicated for deep extensive or localized infectious diseases, streptococcal and staphylococcal infections, burns of 3rd and 4th degrees, followed by blood poisoning, purulent meningitis, wounds in the chest, inflammation of the eyes and ears.
Side effects of the substance: very often, antibiotic treatment leads to a violation of the intestinal microflora or allergic reactions, the same applies to penicillin. Interestingly, an allergy to penicillin is an occupational disease of workers working in the production of this drug. So, long-term effects of the drug on the body, including long-term treatment, lead to allergies.
Contraindications:
- individual intolerance to the components;
- hypersensitivity to antibiotics;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergic diseases of a chronic nature;
- hives;
- hay fever.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: due to the fact that the substance has the ability to penetrate the placenta to the fetus, there is a risk of its detrimental effect on the born child. Do not use on your own without consulting a doctor;
Indications and recommendations: the best and most effective way of treatment is the introduction of an antibiotic intramuscularly, since it, directly entering the bloodstream, quickly penetrates into all parts of the body and attacks infections. Before the first use, be sure to test for the sensitivity of the body to this drug. The antibiotic can get into the fluid of the spinal cord. But the impact is minor. To affect the abdominal cavity, additional local administration is necessary, since through the blood it is ineffective in combating infections in such areas.