Did you know that when you move a certain file on your computer to the trash and empty it, it is not completely deleted?
Computers don’t usually delete files: when you move a file to the trash, your computer simply makes that file invisible and allows the space it occupied to be overwritten for some other data in the future. Therefore, it may take weeks, months or even years before this space is occupied. Until that happens, the "deleted" file is still on your drive; it is simply invisible for standard operations. By following a few simple steps with the right software, you can recover this "deleted" file.
So how do you accurately and safely delete a file permanently? You need to make sure that the space allocated for it earlier will be immediately occupied. Your operating system probably already has the right software that can do this. It is able to “occupy" all the freed space on your disk with other data and, thereby, reduce the chance of successful recovery of deleted data.
We advise you to use BleachBit, an open source secure data deletion tool for Linux and Windows. BleachBit can be used to quickly and safely delete individual files. It can also help you implement periodic secure deletion policies. Alternatively, you can create your own custom file deletion instructions. More information about this is on the tool’s website.
Note! The instructions below are only suitable for completely erasing data from spinning disks (HDDs). They only apply to traditional hard drives, not solid state drives (SSDs). SSDs are often used in computers, USB sticks or flash memory cards. Securely deleting data on SSDs, USB flash drives, and SD cards is different because these types of drives use a technique called "wear leveling" and do not provide low-level access to the bits stored on the drive. What problems may arise during the deletion of data from these media, you can read here.
Installing BleachBit
You can download BleachBit for Windows by downloading the program’s installer from this link.
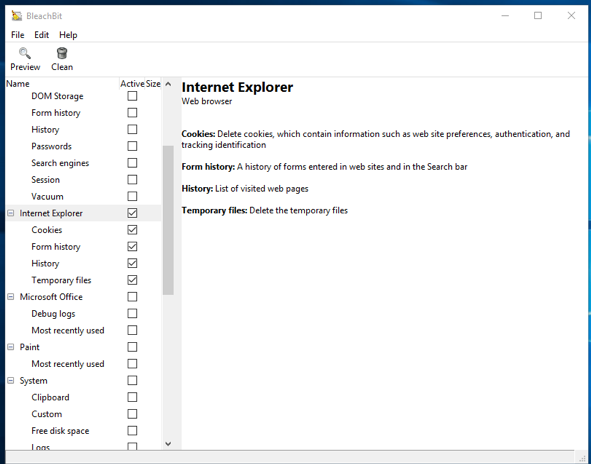
After installation and launch, the main menu of the program will appear in front of you. BleachBit, which will show you frequently used programs and what data they contain.
Using presets
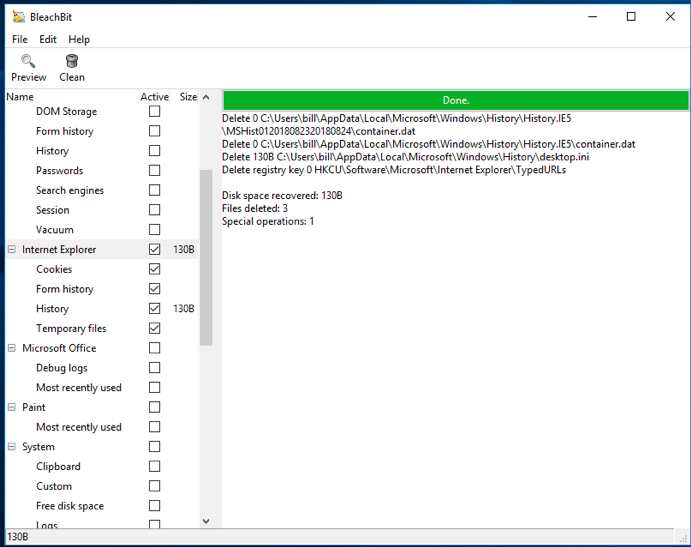
BleachBit can erase the marks left by Google Chrome using Google Chrome presets. Check the box next to Google Chrome. Please note that all items (cookies, form history, request history and temporary files) are checked. You can set up cleaning only certain components as needed. After that, click on the " Clear " button.
BleachBit will delete all the data you have selected.
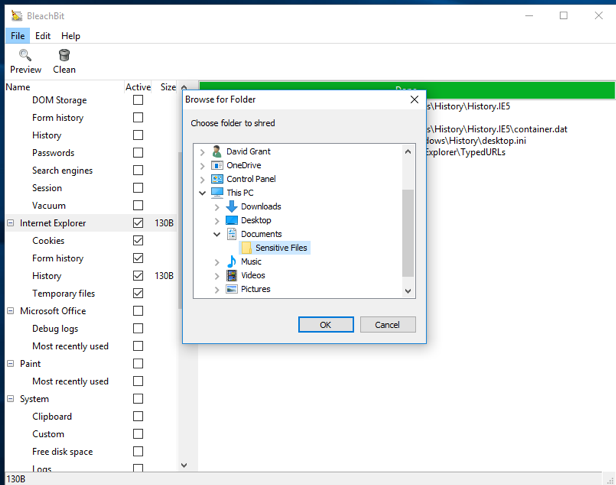
How to Safely Delete a File Folder
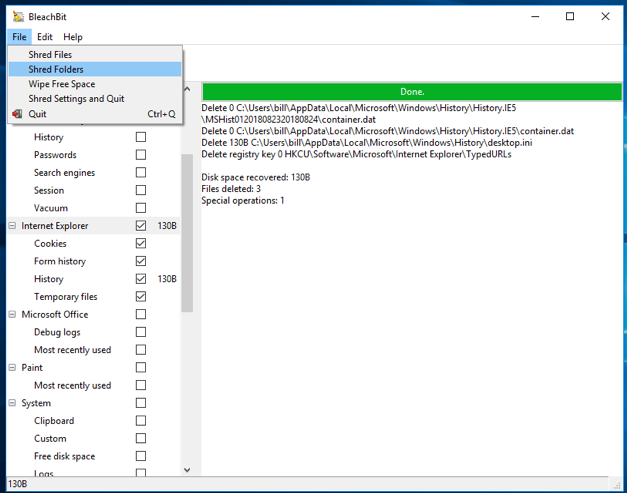
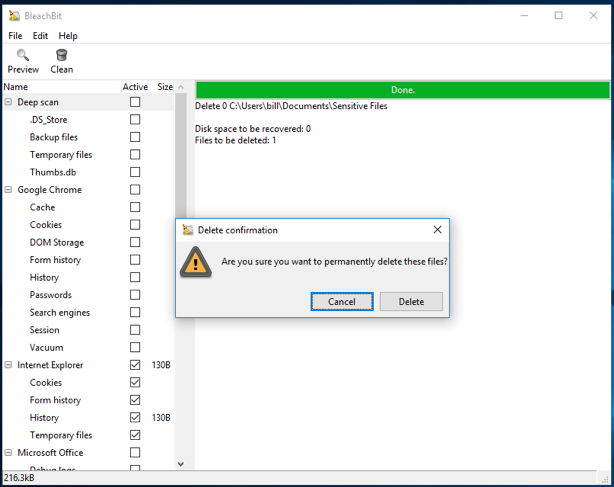
Open the Files menu in the program and select Shared Folders. A small window will open. In it, select the folder you want to delete. BleachBit will ask you to confirm that you want to delete the selected files permanently. Click on the " Delete " button.
After that, the program will show you the files that you have already deleted. Please note that BleachBit deletes each file in the folder individually, and then the folder itself.
BleachBit has a number of other features as well. The most useful of these, in our opinion, is free space sweeping. This will allow you to clean up any remaining traces of files that you have already deleted. Often , the system leaves particles of deleted files in the remaining free space on the hard drive. Clearing free space will overwrite these supposedly "empty" parts of the hard drive with random data. Clearing free space may take some time, depending on how much free space is left on your drive.
Remember that the tips above will help you delete files located in a specific location on your computer. You will not be able to delete backup copies of these files stored elsewhere on your computer, another drive or USB drive; on an email server, in the cloud, or in a conversation with your friends. To safely delete a file, you must get rid of every copy of it wherever it is saved or sent. Also, there is no guarantee that files stored in the cloud (like Dropbox) will be permanently deleted.
Unfortunately, there is one more nuance. Even if you follow the advice above and delete all copies of the file, there is a chance that certain traces of the deleted files may remain on your computer. This is not because the files themselves weren’t properly deleted, but because some part of your OS or some other program intentionally saved the data.
There are many ways this could happen, but two examples should suffice to show you the possibility. On Windows or macOS , Microsoft Office can keep a link to a file name in the Recent Documents menu even if that file has already been deleted (Office can sometimes even save temporary files). For example, LibreOffice can store as many documents as Microsoft Office, which includes filenames even if they have been deleted. In practice, there may be dozens of programs that behave this way.
It’s safe to assume that even if the file has been deleted, its name will probably continue to be stored for some time on your computer. Overwriting the entire drive is the only way to be 100% sure that the filename has also been removed.
Some of you may be wondering, "Can I search my computer for copies of files that I have already deleted?" Answer: yes and no. The search will tell you if the files are actually present on the disk, but you will not be able to find out if this data is stored in any program in compressed or encoded form. Also, be careful that the search itself does not leave fragments of the file on disk! The probability that the contents of the searched file can be saved is lower, but it still exists. Overwriting the entire drive and installing a new operating system is the only way to be 100% sure that file data has been permanently deleted.
Safe deletion of files when dismantling old equipment
If you want to get rid of old equipment or sell it on Avito, you must make sure that no one can extract your data from it. Studies have repeatedly shown that computer owners do not usually delete their files – hard drives are resold chock-full of "confidential information." Therefore, before you sell or dispose of your computer, delete all your data.
For example, if you have a computer that has already reached the end of its life and is no longer being used by you, it would be safer to clean out its hard drive before hiding the machine in a corner or closet. Darik’s Boot and Nuke is a tool designed to clean up hard drive data. There are plenty of tutorials on the internet on how to use it. For example, you can read this guide.
Some disk encryption programs allow the user to destroy the master key, making the encrypted content impossible to decrypt. Since the key itself weighs very little, it can be destroyed almost instantly. This will be an alternative to overwriting data on the drive with software such as Darik’s Boot and Nuke. However, this option is only possible if the data on the hard drive has always been encrypted. If you have not used full encryption before, this option is not suitable for you.
Deleting data from CDs or DVDs
When it comes to deleting data from CDs or DVDs, you should simply shred them. There are inexpensive shredders that can do this just fine. Never throw CDs or DVDs in the trash unless you’re sure they don’t contain any important information.
Securely Erase Solid State Drives (SSDs), USB Flash Drives and SD Cards
Unfortunately, due to the fact that solid state drives, USB flash drives and SD cards work differently, it is very difficult to completely delete individual files from them. As a result, encryption is the best choice in terms of security. This way, if the file is still on the disk, it will be protected from the eyes of scammers who will have access to it but will not be able to decrypt it.
As we mentioned earlier, SSDs and USB sticks use a method called "wear leveling". It works like this: the space on each disk is divided into blocks, like chapters in a book. When a file is written to disk, it is assigned to a specific block or set of blocks (chapters). If you want to overwrite a file, then all you have to do is tell the disk to overwrite those blocks. But in SSDs and USB sticks, erasing and overwriting the same block can cause it to wear out. Each block can only be erased and rewritten a limited number of times before it stops working.
To prolong life, SSDs and USB sticks try to make sure that the number of times data on each block is erased and overwritten is about the same. As a side effect, sometimes instead of erasing and overwriting the block where the file was originally stored, the disk will leave that block alone and mark it as invalid for writing. Then the modified file is simply written to another block. In general, there is no guarantee that the file will actually be overwritten on the new block, which is why secure deletion from SSDs is much more difficult.
If you found this article helpful, feel free to share it with your friends or on social media.
Sourced from ELECTRONIC FRONTIER FOUNDATION.