Mozilla Firefox is considered by many experts to be the best browser out there. It combines powerful user privacy protection features with a high level of security and regular updates. The latest version of Firefox is fast and includes a whole host of features to help you surf the Internet privately and securely.
Another great thing about Firefox is that it’s highly customizable, which is the reason for creating this guide. Below we will take a closer look at how a user can change Firefox settings so that the browser provides a high level of security and privacy, while remaining comfortable for browsing the web.
But before we get to the point, let’s take a look at some important information about setting up Firefox.
note
There are many factors to consider when configuring Firefox to suit your needs, including your threat model and browsing preferences. In other words, there is no "universal" configuration that will suit everyone. This guide is an overview of the features that can be used for various browser configuration options.
Before you start changing Firefox settings and installing a bunch of different add-ons, it’s important to know what Browser Fingerprinting is.
Browser Fingerprinting
The topic of Browser Fingerprinting is relevant because it includes various ways to track and identify a user using his browser and the selected settings. All add-ons you install on your browser and settings changes you make to Firefox are inputs that can potentially be used to identify and track your activity.
This is the catch-22: the more add-ons you install and the more you change your browser settings, the more likely you are to stand out from the crowd and be easier to track. There are special programs to solve this problem – and the latest version of Firefox includes third-party tracking protection features and hides your Browser Fingerprinting.
More is not always better
When we talk about browser add-ons, don’t be like a kid who puts any possible dope in his ice cream. More is not always betterif we are talking about the number of extensions for the Firefox browser.
Having too many add-ons can slow down the performance of the browser and cause it to crash. Many popular Firefox extensions perform the same functionality and are redundant when used together.
Therefore, it is better to keep a balance. Install plugins and change only those parameters that you think will help in a particular case.
be careful
Changing some settings can drastically change the way you browse the web and cause some websites to fail to load. Thus, incremental changes to the settings are the best approach to modifying the browser. You can continue to install add-ons and change settings as long as you make sure that past modifications have taken effect and work correctly.
It is possible to add sites to the list of exceptions – they will not use the plugins you installed.
Firefox privacy settings
Before using Firefox, you may want to change the settings below to improve your privacy.
Note: If you are a macOS user, you will see the word " Preferences " in your menu, not " Options " as mentioned below.
Disabling telemetry
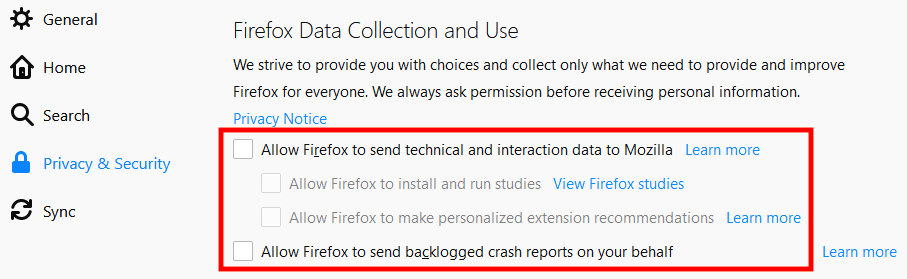
Firefox shares "technical and user activity data" with Mozilla by default. This includes the ability to conduct various kinds of research, among which is the analysis of the activity of your PC. You can learn more about this kind of research here. In addition, there is also a page that talks about Mozilla’s data collection practices . In any case, we recommend that you disable these features.
To do this, navigate to the following path: " Settings " > " Privacy and Security " > " Firefox Data Collection and Use ". Then uncheck the options as shown in the picture below.
You can also turn off telemetry in your Android browser by going to the following path: " Settings " > " Privacy and Security " > " Data Collection " and then unchecking all three options.
Note: You can disable telemetry in the " About: Config " settings in the toolkit.telemetry.enabled parameter, which should be set to " False ".
Changing the default search engine
Firefox currently uses Google as its default search engine, but you can use other private search engines instead.
To do this, go to the following path: " Settings " > " Search " > " Default search engine ". Firefox doesn’t provide many alternatives to the user directly in the settings area. However, you can view additional options by going to the Search Engines section and then selecting the Find Other Search Engines option to view the available alternatives.
Firefox has even published a guide to changing search engine settings.
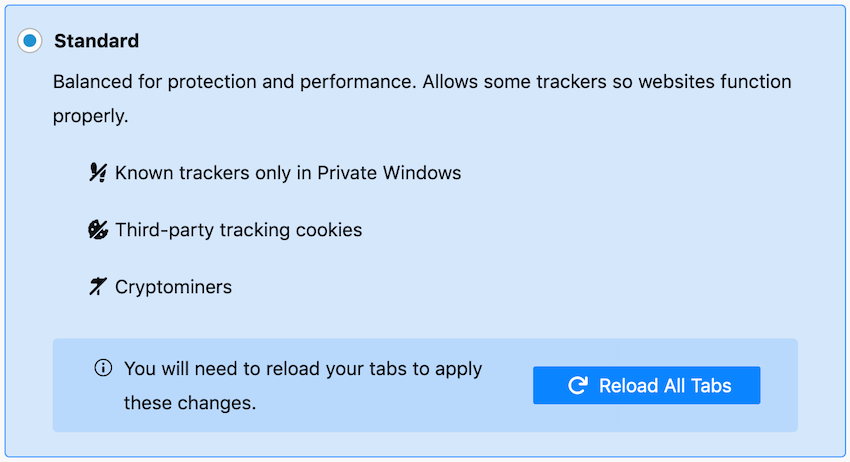
Firefox content blocking
Another great feature of Firefox is blocking inappropriate content. This customizable option will automatically block any content that might track your activity and the sites you visit. There are three data filtering modes: standard, strict and personal. You can block:
- Trackers
- Cookies
- Cryptominers
- "Browser Fingerprints"
To configure content blocking settings in Firefox, go to the following path: " Settings " > " Privacy and Security " and then select the mode you want to use.
Standard mode is a great option for everyday use. Firefox warns that strict mode can cause certain sites to fail when loading.
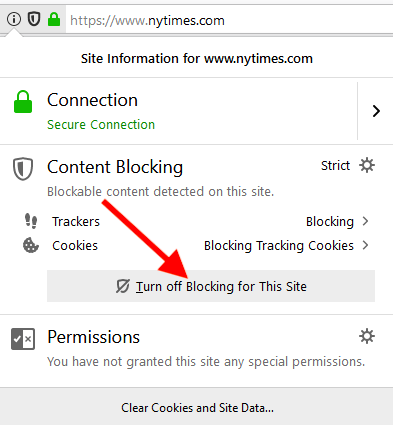
Disable content blocking for specific sites
You can easily disable content blocking on trusted sites. Just enter the URL of the resource, and then click on the " i " icon to the left of the address bar and click on the gray button to stop blocking content.
Another benefit of Firefox’s content blocking feature is that the browser allows you to save your input and automatically increases page loading speed.
"Do Not Track" request
Firefox can also send a request to sites not to track your activity. This is done very simply: a special field is added to the HTTP header. However, the key point when discussing this feature is that it does not, in fact, block tracking. Many websites simply ignore such requests.
Among other things, this feature can make your browser footprint on the web more visible. Therefore, we recommend turning it off so as not to attract additional attention.
You can learn more about the Do Not Track request by clicking here.
Menu "About:Config"
In addition to the settings in the main menu that we talked about earlier, you can also make a number of different changes by opening the About:config section.
Note. If you have made all the above changes to your browser settings, you will be able to see that the status of some settings has already been updated in the "About:config" menu as well. Next, we will also talk about how you can configure Firefox directly from this section. Some options will be repeated as there is a whole group of users who change system settings directly from the About:config menu .
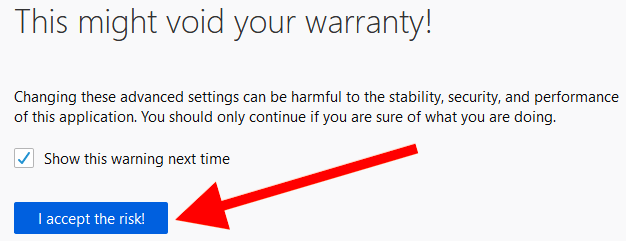
To access these settings, type " about:config " into the URL bar and press the " Enter " button. You will see the inscription ” Proceed with caution ", you should select the option ” Accept the risk and continue ” to start changing browser settings.
After that, you will see a large list of settings, each of which has a status, type and value.
The available options are listed in alphabetical order. In addition, at the top of the page you will find a search bar, with which you can instantly find the option you need.
You can change any browser setting by double-clicking on it with the left mouse button. If the option is of boolean type, then double-clicking will change its value to " True " or " False ". If the option is of type " Integer " or " String ", then double-clicking will open a special field for changing its value.
Below are the settings we think should be changed.
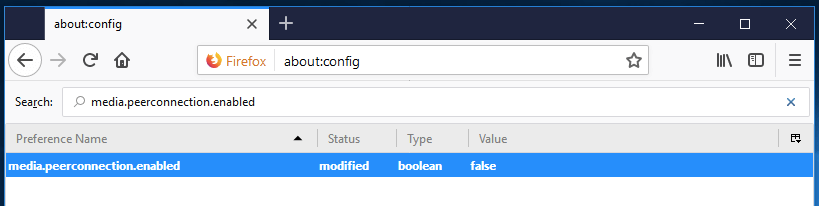
The Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) feature allows users to make video calls, make voice calls, and send files over a P2P network. Unfortunately, using this option may expose your real IP address via STUN requests, even if you are using a good VPN service. A similar problem is called a WebRTC data leak.
To disable the WebRTC option in Firefox, type " media.peerconnection.enabled " into the search bar and then double click on the found option to change its value to " False ".
In addition to Firefox, the WebRTC vulnerability affects other Chromium -based browsers such as Chrome, Opera, Brave, as well as Safari.
privacy.resistFingerprinting = true
Changing this setting to True will help make Firefox’s footprint less visible on the web.
Note. There are many factors that affect the size of a browser fingerprint and the ability to accurately identify you. This is just one way to reduce your footprint on the web.
privacy.trackingprotection.fingerprinting.enabled = true
Another feature that helps keep you private and reduces your browser fingerprint.
privacy.trackingprotection.cryptomining.enabled = true
With its help, the user can block the use of cryptominers on websites.
privacy.firstparty.isolate = true
Changing this feature to True will isolate cookies for the First Party domain, which prevents your activity from being tracked on other domains. This isolation affects many components: Cookies, cache, HTTP authentication, DOM storage, Flash Cookies, SSL and TLS session resumption, Shared Workers, BLOB URIs, SPDY and HTTP/2, automatic cross-origin redirection, window.name, auto-completion of forms, HSTS and HPKP supercookies, broadcast channels, OCSP, favicons, media resource URIs, speculative and prefetched connections.
This option was first added in late 2017 as part of the Tor Uplift project .
privacy.trackingprotection.enabled = true
Built-in tracking protection from Mozilla. For its correct functioning, the Disconnect.me filter list is used. Needless to say, it might even be redundant if you’re already applying uBlock Origin filters .
geo.enabled = false
By setting this parameter to False, the user will not be able to track his location, information about which can be requested by the site he opened. As Mozilla explains, this option is enabled by default. The browser uses Google’s location service to calculate your geolocation. To do this, Firefox sends to Google:
- your computer’s IP address;
- information about nearby Wi-Fi points;
- a random client ID assigned by Google (expires every two weeks).
Before the data is sent to Google, you will receive a request from the site you are visiting. Therefore, you can still be in control even if your location is being tracked.
By setting this parameter to False, you will prevent websites from accessing your microphone and camera.
This is an option of integer type with different value options. There are several options for cookie values:
- 0 = Accept all cookies by default.
- 1 = Only accept cookies from a specific site (block third-party cookies)
- 2 = block all cookies by default
- 3 = block cookies from previously unfamiliar sites
- 4 = New Cookie Storage Policy (prevent trackers from accessing storage)
To increase your privacy level, set a value between 1 and 4. For example, a value of 4 will give you full tracking protection, but it can also cause certain sites to fail to load. You can read more about this here.
This is another integer type option and should be set to 2. It allows the user to decide when cookies are deleted. The following options are possible:
- 0 = always accept cookies;
- 1 = All Cookies must be approved
- 2 = Only accept cookies during the current session
- 3 = accept cookies for N-number of days
If set to 2, the websites you visit should open without any problems. All cookies will be automatically deleted after the session ends.
network.dns.disablePrefetch = true
By setting this parameter to True, the user will prevent Firefox from "prefetching" DNS. While activating this feature may improve page loading speed, it also comes with some risks, which are described in this article.
network.prefetch-next = false
Similar to DNS prefetching, setting this to False will give you the option to prevent Firefox pages from being prefetched . Mozilla has added this feature to speed up the loading of web pages that you frequently visit. However, its use poses a threat to your privacy. A vivid example of how privacy has to be sacrificed in order to improve the quality of the browser.
webgl.disabled = true
Using WebGL is a potential security risk, so it’s best to disable this feature by setting webgl.disabled to True. Another problem with WebGL is that this option can be used to track your phone’s activity.
You can read more about it here and here.
dom.event.clipboardevents.enabled = false
With this feature, you prevent websites from being notified when you copy, paste, or cut from their pages.
This option disables automatic playback of DRM-related HTML5 content. You can read more about this here.
Firefox Safe Browsing Settings
Many experts recommend disabling Firefox’s Safe Browsing feature due to privacy concerns and potential Google tracking. However, such concerns are not relevant – they were based on older versions of the browser that used "real-time URL search". This method has not been used since 2011.
When searching for a specific URL, Firefox takes the following precautions to protect user privacy (according to François Marie, Mozilla security engineer):
- Query string parameters are stripped from URLs, which are themselves further checked as part of the base security feature.
- The Safe Browsing Cookies are stored separately so they don’t get mixed up with other Standard Browsing Cookies.
- When requesting the full hash for a 32-bit prefix, Firefox adds a few extra "noise components" to further obfuscate the original URL.
Therefore, we have come to the conclusion that disabling Safe Browsing will not give you any tangible privacy benefits, and will also create an additional security risk. However, if you still want to disable this feature, you can do so in the " about:config " menu:
- safebrowsing.phishing.enabled = false
- safebrowsing.malware.enabled = false
High-level privacy and security extensions in Firefox
There are several great add-ons for the Firefox browser that provide a high level of user privacy and security.
Note. When looking for extensions for Firefox, keep in mind what changes you have already made to your browser settings. Some of them may be redundant, overload the program and lead to errors in work.
Combined with the settings changes above, we recommend that you install the following extensions to improve your privacy level:
- uBlock Origin
- HTTPS Everywhere
- Decentraleyes
All three extensions are in addition to the settings listed above, are easy to use, and probably won’t break websites you visit regularly.
It is worth mentioning separately one more worthwhile addition – Cookie AutoDelete. However, if you have already changed your cookie settings in the "about:config" menu (as described above), then you will not need it.
uBlock Origin
uBlock Origin is an effective plugin that blocks both ads and trackers. It has gained popularity as a decent alternative to Adblock Plus, allowing it to host "acceptable ads" that many users don’t like. One of the bonuses of uBlock Origin is that the add-on can significantly improve browser performance and web page loading speed.
In addition, in uBlock Origin, the user can whitelist certain websites. Considering that many resources deny access to them if they detect an ad blocker, the option to whitelist a site will definitely come in handy. uBlock Origin is free and open source.
HTTPS Everywhere
HTTPS Everywhere is a great Firefox add-on. It establishes an HTTPS connection to the websites you visit, as long as HTTPS is available for them.
Fortunately, more and more websites are adopting HTTPS technology. However, HTTPS Everywhere is still a useful extension to use in Firefox.
You can get more information about HTTPS from the Electronic Frontier Foundation, which is responsible for creating this program.
Decentraleyes
Decentraleyes is an interesting Firefox add-on that protects you from being tracked by content delivery networks operated by third parties. While CDNs do help improve page loading speed and browser performance, they are usually offered for free by third parties that use the data they collect to track your online activity. Among such companies that are trying to get information about you are Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Cloudflare, Yandex, Baidu, MaxCDN.
Decentraleyes solves your privacy problem by hosting CDN resources locally. As described in their own GitLab repo, Decentraleyes "intercepts traffic, finds relevant resources locally, and injects them into the environment ", thereby preventing CDN users from being tracked.
Cookie AutoDelete
You will not need this add-on if you have made the above changes to your settings to automatically delete cookies after your session ends.
However, if you prefer using add-ons instead of making changes to your browser settings, then AutoDelete Cookie is a great choice. The extension removes cookies that you no longer need, thereby protecting the user from tracking.
Privacy Badger
Privacy Badger is another add-on from the Electronic Frontier Foundation that blocks ads and trackers. One of the downsides of the extension is that it only blocks third-party sites. For example, Google Analytics sites will not be blocked. Another disadvantage of Privacy Badger is that the plugin doesn’t actually use the filter list. Instead, it mostly learns as you apply it.
It’s worth noting that Privacy Badger is very easy to use and goes a long way in providing a high level of privacy while browsing the web. It can be used in combination with uBlock Origin, although there are some similarities in terms of functionality.
The Matrix
uMatrix is an advanced add-on that gives you control over queries that can track activity on the sites you visit. It was developed by the same people behind uBlock Origin. One of the advantages of uMatrix is that the extension is very easy to customize for a specific use case.
One of the disadvantages of the program is that setting it up for regular daily browsing on the web can be difficult and time consuming. However, if you need a powerful ad and tracker blocker and don’t mind figuring out new software, then feel free to install uMatrix.
NoScript
NoScript is a powerful script blocker. It allows you to identify and block active scripts on various websites. Although the add-on gives you control over the sites, blocking a certain element can lead to an error. This breaks many sites, requiring you to configure additional settings. If you’re already using uBlock Origin or uMatrix, then you probably shouldn’t use NoScript as it will only hurt browser performance.
You also need to be prepared to take the time to fully understand how NoScript works.
New Firefox privacy features
Firefox has added several new privacy features, among them DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and Firefox Private Network. Interestingly, these functions are based on the infrastructure of Cloudflare, a large US company that provides CDN services.
Firefox Private Network (VPN)
Firefox has officially launched a proxy server extension called Firefox Private Network, which many refer to as Firefox VPN. While this option may be useful to many users, we have identified a few shortcomings in the Firefox VPN guide:
- Browser-only encryption. Encrypted traffic coming only through the Firefox browser. So it’s a proxy, not a VPN.
- cloudflare. All traffic is routed through Cloudflare.
- Data collection (logs ). As stated in the privacy policy, Cloudflare will log your source IP address and the sites you visit. Mozilla also records several types of data: technical data, interaction data, registration data.
- Location cannot be selected. Unlike other browser-based proxies, Firefox does not give you the option to select a specific location. It is either displayed or hidden.
Cloudflare and Mozilla, based in the United States (Five Eyes), are at great risk of being required by the government to obtain information about user data (as has already happened with Lavabit, as well as Riseup ). Firefox Private Network is still in beta and is only available to US users.
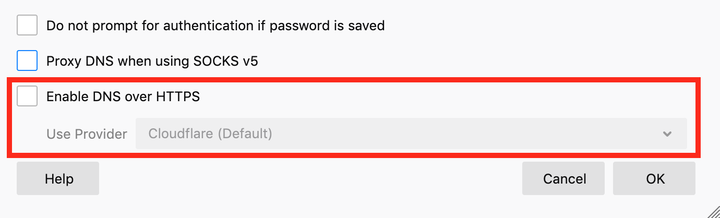
DNS over HTTPS (DoH)
As with Firefox Private Network, the implementation of DNS over HTTPS is entirely dependent on Cloudflare ‘s infrastructure. In effect, this makes Cloudflare the central point for handling all DNS requests for the default Firefox browser.
Although the DNS over HTTPS feature may seem useful, at first glance, there are also potential risks when using it. This is discussed in an article titled " Centralized DoH is bad for privacy " (published in 2019), which concludes as follows:
“DoH centralization at this point in time has a negative impact on user privacy, as anyone who can see your metadata is still able to do so, even when the DNS is sent to a third party. In addition, this third party accesses the per-device log and all DNS queries, so that the gadgets themselves can be tracked by their IP addresses. Even if possible data leaks are fixed, sending the DNS to a third party remains at best a temporary solution that should not be seriously relied upon. This does not provide a high level of security, since it is very difficult to account for all content providers, especially those that are not related to the CDN. DNS encryption can greatly increase your level of privacy if no third parties are involved.
Many people assume that an encrypted third-party DNS will be able to provide them with complete privacy and anonymity. This is a false assumption. Their IP address and location are still exposed – the ISP can still see the websites you visit (IP addresses), even if it no longer handles DNS queries. Also, any good VPN will provide much better protection than Cloudflare’s DoH.
To disable DNS over HTTPS (DoH) in Firefox, go to the following path: " Settings " > " General " and then scroll down to network settings. In the window that opens, find the "DNS over HTTPS (DoH) " option and disable it.
Additional Information
Below are resources with more information on setting up Firefox for a high level of privacy and security:
- js Firefox hardening. As written on their GitHub page, this is "a configuration file that will help manage hundreds of Firefox settings." For more information about it, you can follow this link.
- privacy settings. This is a Firefox add-on that gives you easy access and control over the browser’s built-in privacy settings.
- Firefox Profile Maker. FFprofile helps you create a Firefox profile with privacy and security settings to suit your needs.
Conclusion
In our opinion, Firefox remains one of the best all-round browsers on the market. It can provide a high level of privacy if configured according to the guidelines above.
While many of the options and add-ons described in this guide can greatly increase your privacy, one problem remains: hiding your IP address and location. This requires a good VPN service. The Tor network can provide you with complete anonymity, but it has several drawbacks in the form of slow page loading speeds, constant risks and limitations (only works in the browser).
Based on Restoreprivacy.